Describe How the Schwann Cells Form the Myelin Sheath
Myelinating and non-myelinating Schwann cells are the 2 kinds of Schwann cells. Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath encasing the nerve fibers.
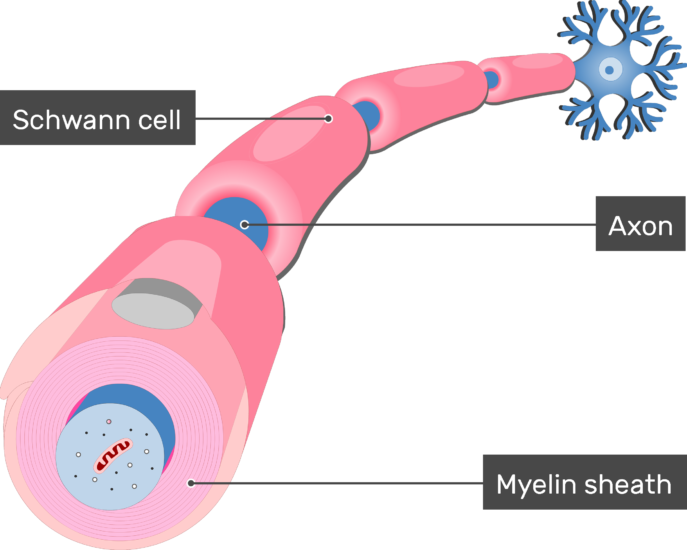
Myelination Of Axons By Schwann Cells
Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells are types of neuroglia cells that produce myelin sheath which acts as insulation along the axon.
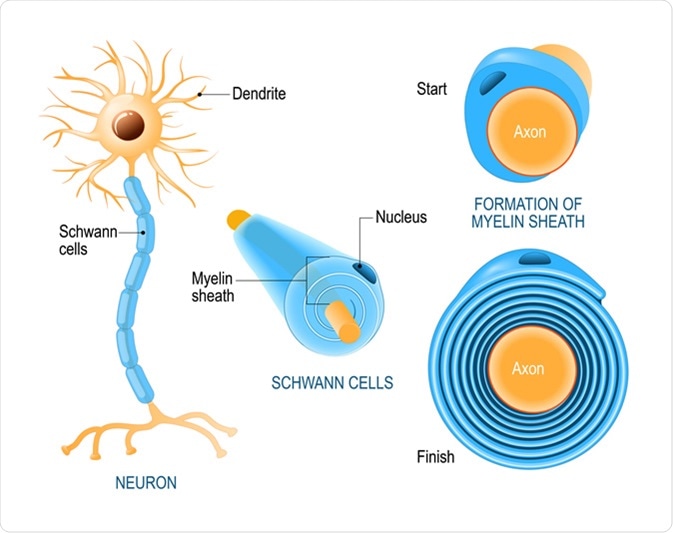
. Sanary oper id 9. In the PNS they are Schwann cells. Schwann cells form a sheath around the axon which is known as the myelin sheath.
Myelin itself forms by the spiral wrapping around an axon of an enormously expanded glial plasma membrane that then compacts. Structure of a Nerve 10. In the CNS glial cells are oligodendrocytes.
It is important that myelin sheath is formed on axons to aid the conduction of electrical signals. The myelin membranes originate from and are a part of the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system and the oligodendroglial cells in the central nervous system see Chap. These are both what are packed around the axon to form the myelin sheath from the cell.
Cell body nucleus nucleolus chromatophilic substance dendrites initial segment of axon myelin sheath myelin. About Us Trending Popular. Schwann cells are a type of glial cells of the peripheral nervous system that help form the myelin sheath around the nerve fibers.
Expert Answer 100 3 ratings The Schwann cells wrap themselves tightly around the axon like a jellyroll. Binds groups of axons to form bundles of fibers called fascicles. As it moves this leading edge slides underneath the outer portion of the Schwann cell pushing it out of the way.
2 um or larger undergo a wrapping process called myelination. Most mammalian nerves are surrounded by a whitish fatty layer called the myelin sheath not part of the neuron The myelin sheath insulates the nerve fibres to prevent signal loss or crossing of signals. Extrinsic signals from the axon and the extracellular matrix drive Schwann cells to adopt a myelinating.
Schwann cells that surround large diameter axons A and B fibers. Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma. The myelin sheath is formed by myelinating Schwann cells wrapping across the axons of sensory and motor neurons.
Wrap themselves tightly around the axon in jelly roll fashion. Schwann cell and myelin sheath are two types of structures in the axon of the neuron. Schwann cells are named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann who discovered them in the 19th century.
Label the following structures on the diagram of a multipolar neuron shown below. Myelin sheath of the neuron. Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma.
Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath encasing the nerve fibers. Binds fascicles by forming a cord like nerve. Neurilemma is the collective term used for cytoplasm and nuclei present around the myelin sheath which helps in the regeneration process of nerves.
This plasma membrane contains high levels of fat which is essential for the construction of myelin sheath. During the wrapping process the. Schwann cells or neurilemma cells are the cells which form the myelin sheath around neuronal axons in the peripheral nervous system PNS only.
Schwann cells are cells in the peripheral nervous system that form the myelin sheath around a neurons axon. A Schwann cell forms a myelin sheath by wrapping its plasma membrane concentrically around the inner axon. If youve ever noticed the jerky sudden movements babies make this is because their myelin sheaths arent fully developed at birth.
Furthermore Schwann cells produce myelin while myelin sheath increases. The main difference between Schwann cell and myelin sheath is that Schwann cells wrap around the axon of the neuron to form the myelin sheath while myelin sheath serves as an electrically insulating layer. A Schwann cell becomes apposed to an axon and envelopes it in a trough.
Essentially the inner layers of the wraps of Schwann cells are typically the membrane which forms the myelin sheath whilst the outer layers form the nucleated cytoplasmic layer called the neurilemma. View the full answer Previous question Next question. Schwann cell also called neurilemma cell any of the cells in the peripheral nervous system that produce the myelin sheath around neuronal axons.
Throughout the downstream portion of the human dystrophin gene the Schwann cell promoter is found which results in shortened transcripts that are synthesised in a tissue. Thus the key difference between Schwann cells and myelin sheath is that Schwann cells are the peripheral nervous system cells which form the myelin sheath around the axon while myelin sheath is an electrically insulating layer wrapped around the axon which increases the speed. Nodes of Ranvier The key thing to note here is that the cells that produce myelin in.
As they get older and the myelin matures and builds up their movements become smoother and more controlled. For the myelin sheath to be created by Schwann cells in the PNS the plasma membrane of these cells needs to wrap itself around the axons of the neuron concentrically spiralling to add membrane layers. Surrounding axon around myelin sheath.
They form as the result of reciprocal interactions between axons and Schwann cells. 1 Phoca Answer. Each Schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath around an axon.
The myelin sheath is a greatly extended and modified plasma membrane wrapped around the nerve axon in a spiral fashion. While the nucleus remains fixed the inner turn of the glial cell membrane spirals around the axon to add membrane layers or lamellae to the myelin sheath. 1 2 3 The process begins when one part of the Schwann cell begins to move along the surface of the axon.
The sheath it packed tightly in spiral casings around the axon. Schwann cell myelination Myelinated nerve fibers are essential for the rapid propagation of action potentials by saltatory conduction. It then begins to rotate around the axon wrapping it loosely in successive layers of its plasma membrane.
Schwann cells are individualized as single myelin sheath to form the axon. Schwann cells are another name for neurilemma cells. Each myelin-generating cell furnishes myelin for only one.
Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath encasing the nerve fibers. Myelin is formed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system PNS and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system CNS. A schwann cell envelops and rotates.
Solved Sensory Receptor Effector Organ 9 Describe How The Chegg Com
Solved Sanary Oper Id 9 Describe How The Schwann Cells Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment